Questions
Base your answers to questions 61 through 63 on the information below.
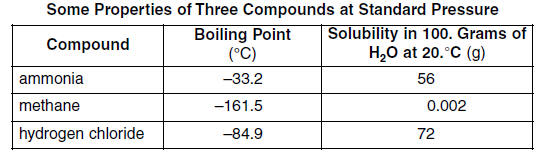
61 Convert the boiling point of hydrogen chloride at standard pressure to Kelvins. [1] HIGHLIGHT TO SEE THE ANSWER
62 Explain, in terms of molecular polarity, why hydrogen chloride is more soluble than methane in water at 20.°C and standard pressure. [1] HIGHLIGHT TO SEE THE ANSWER
63 Explain, in terms of intermolecular forces, why ammonia has a higher boiling point than the other compounds in the table. [1] HIGHLIGHT TO SEE THE ANSWER
|