|
|
Atomic Structure Links Electrons and Sublevels Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table Writing Electron Configurations Box and Arrow Configurations using Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund's Rule Quantum Numbers The 4 quantum numbers are the address of an electron. Quantum numbersThink of the quantum numbers as addresses for electrons The principal quantum number, n (the energy level) determines the size of an orbital (larger n = bigger orbitals) largely determines the energy of the orbital (larger n = higher energy) can take on integer values n = 1, 2, 3, ..., 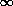 all electrons in an atom with the same value of n are said to belong to the same principle energy level
the azimuthal quantum number, 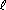 (the sublevel) (the sublevel) designates the overall shape of the orbital within a shell affects orbital energies (larger 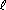 = higher energy) = higher energy) all electrons in an atom with the same value of 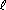 are said to belong to the same sublevels are said to belong to the same sublevels only integer values between 0 and n-1 are allowed sometimes called the orbital angular momentum quantum number spectroscopists use the following notation for sublevels
the magnetic quantum number, m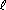 (the orbital (box) the electron is in) (the orbital (box) the electron is in) s sublevel p sublevel d sublevel f sublevel The spin quantum number, ms (the direction of the arrow) several experimental observations can be explained by treating the electron as though it were spinning spin makes the electron behave like a tiny magnet spin can be clockwise or counterclockwise spin quantum number can have values of +1/2 or -1/2 (arrow up or arrow down)
Examples The 4 quantum numbers of the last electron in each sublevel shown below   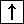
2p
| 2p4 | n =2 | 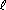 =1 =1 | m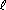 =-1 =-1 | ms =-1/2 |
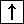    
5d | 5d5 | n =5 | 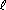 =2 =2 | m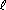 =+2 =+2 | ms =+1/2 |
Atomic Structure Links Electrons and Sublevels Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table Writing Electron Configurations Box and Arrow Configurations using Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund's Rule Quantum Numbers  Chemical Demonstration Videos Chemical Demonstration Videos
|
|

